The problem is given m colors find a way of coloring the vertices of a graph such that no two adjacent vertices are colored using same color. While graph coloring the constraints that are set on the graph are colors order of coloring the way of assigning color etc.
 Pdf Injective Edge Chromatic Index Of A Graph
Pdf Injective Edge Chromatic Index Of A Graph
This is where the vertices of a graph g are assigned different colors so that.
Radio coloring in graph theory. Reviews five real world problems that can be modelled using graph colouring. A coloring is given to a vertex or a particular region. Each edge of a graph has a color assigned to it in such a way that no two adjacent edges are the same color.
Radio labeling of graphs is a specific type of graph labeling. The most common type of edge coloring is analogous to graph vertex colorings. By using the graph coloring the radio frequencies are assigned.
Such a coloring is a proper edge coloring. Graph coloring problem is to assign colors to certain elements of a graph subject to certain constraints. In this video we define a proper vertex colouring of a graph and the chromatic number of a graph.
The basic type of graph labeling is vertex coloring. In its simplest form it is a way of coloring the vertices of a graph such that no two adjacent vertices are of the same color. This is called a vertex coloring similarly an edge coloring assigns a color to each.
With cycle graphs the analogy becomes an equivalence as there is an edge vertex duality. For example you could color every vertex with a different color. Thus the vertices or regions having same colors form independent sets.
It is an assignment of labels traditionally called colors to elements of a graph subject to certain constraints. The towers are considered as the vertices and frequencies are. Graph coloring have the property that no two adjacent vertices will have the same color.
Every graph has a proper vertex coloring. If the vertex coloring has the property that adjacent vertices are colored differently then the coloring is called proper. In graph theory a branch of mathematics a radio coloring of an undirected graph is a form of graph coloring in which one assigns positive integer labels to the graphs such that the labels of adjacent vertices differ by at least two and the labels of vertices at distance two from each other differ by at least one.
Vertex coloring is the most common graph coloring problem. In graph theory graph coloring is a special case of graph labeling. Avoids jargon and technical terms.
In general given any graph g text a coloring of the vertices is called not surprisingly a vertex coloring.
 Pdf Fuzzy Colouring Of Fuzzy Graphs
Pdf Fuzzy Colouring Of Fuzzy Graphs
 Cognitive Radio Networks Spectrum Allocation An Acs Perspective
Cognitive Radio Networks Spectrum Allocation An Acs Perspective
 Pdf A Heuristic Algorithm For The Set T Coloring Problem
Pdf A Heuristic Algorithm For The Set T Coloring Problem
 Improving Probability Learning Based Local Search For Graph
Improving Probability Learning Based Local Search For Graph
Channel Assignment In Wireless Networks Graph Coloring Ppt
 Introduction To Graph And Graph Coloring
Introduction To Graph And Graph Coloring
 Pdf Heuristic Algorithms For Graph Set Coloring Problem
Pdf Heuristic Algorithms For Graph Set Coloring Problem
 Interval Edge Coloring Wikipedia
Interval Edge Coloring Wikipedia
 Pdf A Distributed Approach For Frequency Allocation Using Graph
Pdf A Distributed Approach For Frequency Allocation Using Graph
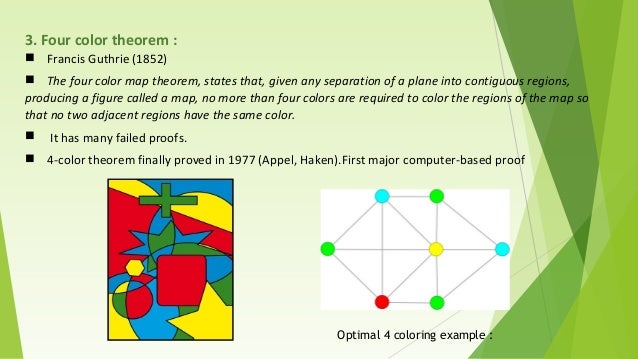 Graph Coloring And Its Applications
Graph Coloring And Its Applications
 Illustration Of Graph Partitioning The Color Of Each Vertex
Illustration Of Graph Partitioning The Color Of Each Vertex
 Discrete Mathematics More On Graphs Tutorialspoint
Discrete Mathematics More On Graphs Tutorialspoint
 A Graph Radio K Coloring Algorithm Springerlink
A Graph Radio K Coloring Algorithm Springerlink
 Pdf Spectrum Graph Coloring And Applications To Wi Fi Channel
Pdf Spectrum Graph Coloring And Applications To Wi Fi Channel
 Graph Coloring Part 1 Vertex Coloring Explanation Youtube
Graph Coloring Part 1 Vertex Coloring Explanation Youtube
 Ppt Graph Coloring And Applications Powerpoint Presentation
Ppt Graph Coloring And Applications Powerpoint Presentation
 Pdf Contemporary Methods For Graph Coloring As An Example Of
Pdf Contemporary Methods For Graph Coloring As An Example Of
 Pdf Applications Of Graph Coloring
Pdf Applications Of Graph Coloring
 Pdf Slides Of Graph Colouring And Frequency Assignment Zib
Pdf Slides Of Graph Colouring And Frequency Assignment Zib
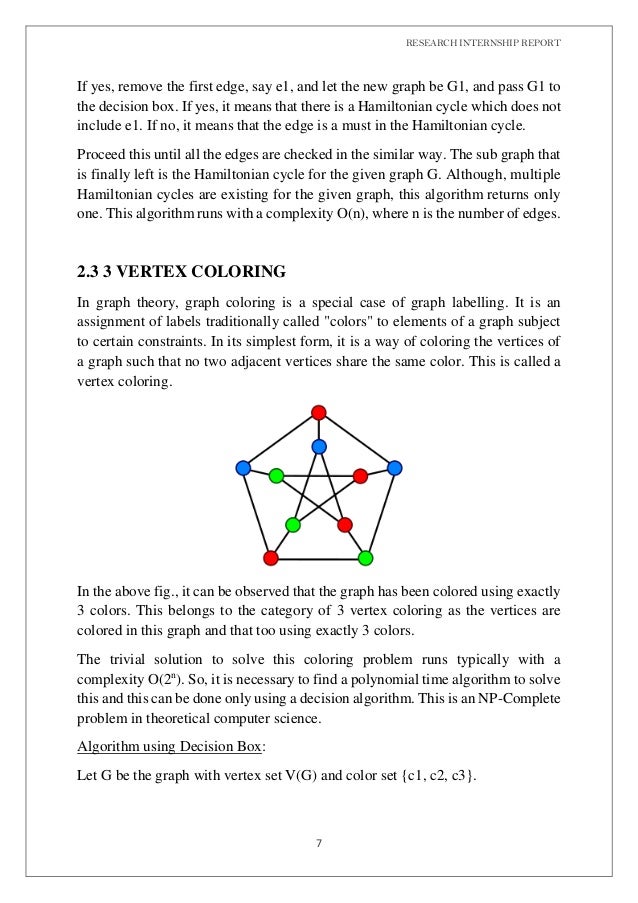 Np Complete Problems In Graph Theory
Np Complete Problems In Graph Theory
 A Lower Bound Technique For Radio K Coloring Sciencedirect
A Lower Bound Technique For Radio K Coloring Sciencedirect
 Graph Coloring An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Graph Coloring An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
 Pdf 3 Consecutive Edge Coloring Of A Graph
Pdf 3 Consecutive Edge Coloring Of A Graph
 Graph Algorithm Tutorialspoint
Graph Algorithm Tutorialspoint
 Pdf Solving Graph Coloring Problems With The Douglas Rachford
Pdf Solving Graph Coloring Problems With The Douglas Rachford
 Graph Coloring With Ants Ppt Video Online Download
Graph Coloring With Ants Ppt Video Online Download
 Programming Java Graph Coloring Algorithms Backtracking And Greedy
Programming Java Graph Coloring Algorithms Backtracking And Greedy

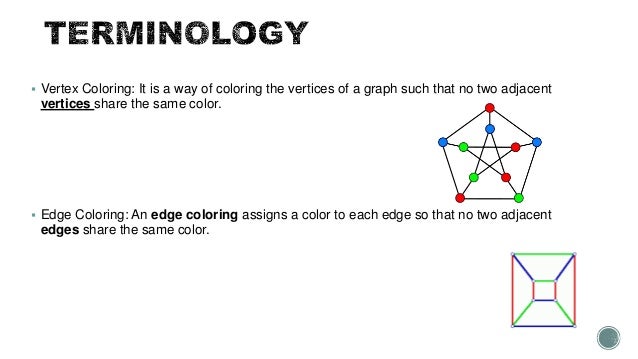
0 Response to "Radio Coloring In Graph Theory"
Post a Comment